Health
Researchers Uncover Why We Flinch at On-Screen Violence
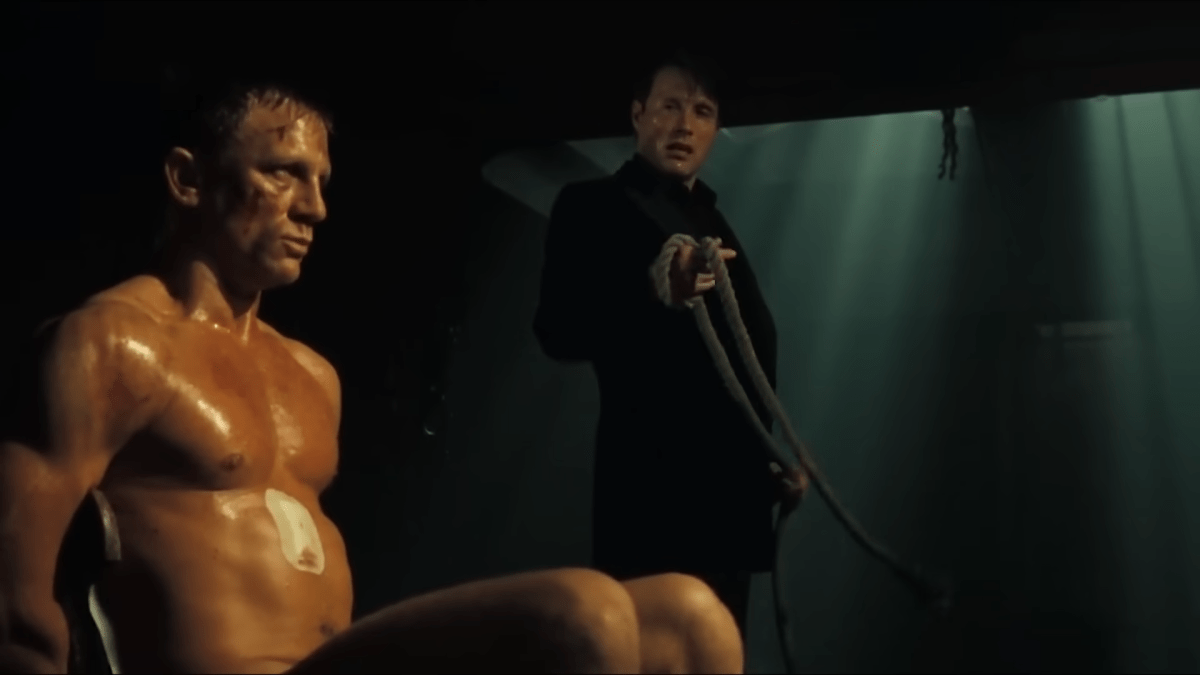
Recent research has revealed significant insights into the neurological responses triggered by viewing violence on screen. A study conducted by the Brain Research Institute at the University of Toronto found that specific areas of the brain activate when an individual witnesses another person experiencing harm. This activation effectively simulates the sensation of pain in the corresponding regions of our own bodies, leading to a physical flinch response.
The study, published in 2023, examined the brain activity of participants while they viewed various forms of on-screen violence. Researchers, led by Dr. Emily Roberts, utilized functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) to measure neural responses. The findings indicated that when subjects observed violent scenarios, their anterior cingulate cortex and insular cortex lit up, mirroring the pain experience in others.
Understanding the Neural Mechanism
These brain regions are integral to the emotional processing of pain and empathy. The results suggest that our brains are wired to respond to the suffering of others, a phenomenon that can be traced back to evolutionary survival mechanisms. By simulating pain in ourselves, we may be better equipped to empathize with others and react to potential threats.
During the experiments, participants reported feelings of discomfort and unease while viewing violent scenes. This aligns with the brain activity observed, reinforcing the notion that witnessing violence, even in a fictional context, can provoke genuine emotional and physical reactions. The study’s outcomes shed light on why many individuals find certain types of entertainment disturbing or difficult to watch.
Moreover, the research underscores the importance of understanding these reactions in the context of media consumption. As the prevalence of graphic content in films and video games increases, insights into our brain’s response can inform discussions about the potential psychological impacts of such exposure.
Implications for Media and Society
The implications of this study extend beyond mere curiosity. As the media landscape continues to evolve, recognizing how on-screen violence affects audiences can shape content creation and regulation. Filmmakers and game developers may benefit from understanding the psychological effects that their work can induce in viewers.
Furthermore, this research may influence therapeutic approaches for individuals who struggle with trauma or anxiety related to violence. By exploring the neurological underpinnings of our reactions, mental health professionals can develop strategies to help individuals process their responses to violence in media more effectively.
As society grapples with the impact of violent content, the findings of this study prompt a broader conversation about responsibility in media production and consumption. Understanding the interplay between visual stimuli and emotional response can lead to more informed choices for audiences and creators alike.
In conclusion, the study conducted by the Brain Research Institute at the University of Toronto offers a compelling glimpse into the human brain’s response to on-screen violence. By mapping the neural mechanisms involved, researchers are helping to unravel the complex relationship between media and emotional processing, prompting necessary discussions about the implications for society and individual well-being.
-

 Health3 months ago
Health3 months agoNeurologist Warns Excessive Use of Supplements Can Harm Brain
-

 Health3 months ago
Health3 months agoFiona Phillips’ Husband Shares Heartfelt Update on Her Alzheimer’s Journey
-

 Science1 month ago
Science1 month agoBrian Cox Addresses Claims of Alien Probe in 3I/ATLAS Discovery
-

 Science1 month ago
Science1 month agoNASA Investigates Unusual Comet 3I/ATLAS; New Findings Emerge
-

 Science1 month ago
Science1 month agoScientists Examine 3I/ATLAS: Alien Artifact or Cosmic Oddity?
-

 Science1 month ago
Science1 month agoNASA Investigates Speedy Object 3I/ATLAS, Sparking Speculation
-

 Entertainment5 months ago
Entertainment5 months agoKerry Katona Discusses Future Baby Plans and Brian McFadden’s Wedding
-

 Entertainment4 months ago
Entertainment4 months agoEmmerdale Faces Tension as Dylan and April’s Lives Hang in the Balance
-

 World3 months ago
World3 months agoCole Palmer’s Cryptic Message to Kobbie Mainoo Following Loan Talks
-
 Science1 month ago
Science1 month agoNASA Scientists Explore Origins of 3I/ATLAS, a Fast-Moving Visitor
-

 Entertainment2 months ago
Entertainment2 months agoLewis Cope Addresses Accusations of Dance Training Advantage
-

 Entertainment3 months ago
Entertainment3 months agoMajor Cast Changes at Coronation Street: Exits and Returns in 2025









