Science
Optimize Welding Precision with Advanced Positioner Solutions
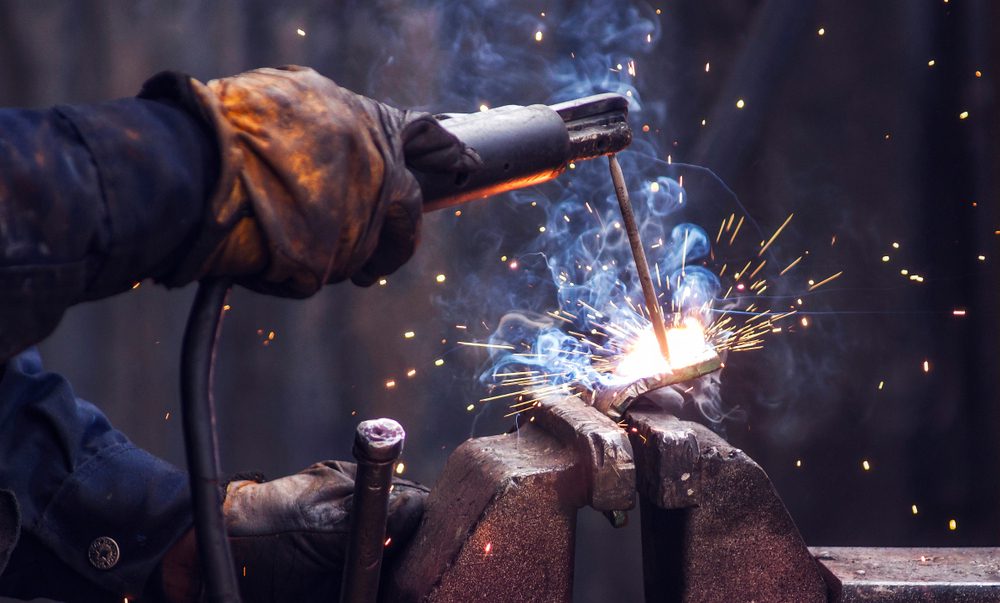

Welding operations are evolving as technology enhances precision and safety in the workplace. A crucial tool in this transformation is the welding positioner, which allows operators to securely hold and rotate workpieces, ensuring optimal angles for welding. This article explores the various types of welding positioners, their features, and the benefits they offer to operators and businesses alike.
Understanding Welding Positioners
A welding positioner is a device designed to hold and rotate workpieces, or ‘weldments’, into the correct position for welding. By securing the workpiece to a rotating table, the operator can access different angles without needing to reposition themselves or manually adjust the workpiece. This not only improves the quality of the weld but is particularly beneficial for continuous welding on complex or circular shapes.
There are several types of welding positioners tailored to different workpiece sizes and functions. Among the most common are:
– **Benchtop Positioners**: These compact, lightweight units are ideal for intricate tasks and can be easily mounted on workbenches.
– **Floor-Mounted Positioners**: Larger and more robust, these units handle medium to heavy workloads and often feature tilt and swivel capabilities.
– **Tailstock and Headstock Positioners**: Designed for fabricating long workpieces, such as pipes and frames, these positioners utilize powered components for efficient rotation.
– **Turntables**: These simple rotary positioners rotate on a single horizontal axis, providing basic functionality for various tasks.
– **Tilt-Rotate Positioners**: Offering the greatest flexibility, these units allow workpieces to be positioned for optimal downhand welding.
Key Features and Benefits
When evaluating a welding positioner, several key features should be considered:
– **Load Capacity**: The maximum weight the positioner can safely handle should exceed the weight of the heaviest workpieces.
– **Rotation Speed**: Adjustable RPM settings are essential for tailoring the speed to specific welding needs.
– **Tilt Range**: A wide range of tilt angles enhances flexibility in workpiece positioning.
– **Table Size**: The diameter of the rotating table must accommodate typical workpieces comfortably.
– **Control System**: Options range from basic foot pedals to advanced programmable logic controllers (PLCs) that automate welding sequences.
Integrating a rotary welding positioner into a workflow offers numerous advantages. Primarily, it reduces the time required to handle and reposition heavy or awkward workpieces. This efficiency allows a single welder to manage tasks that would typically require multiple operators, significantly increasing productivity—potentially by as much as 40%.
In addition to improving efficiency, welding positioners enhance the quality of welds. By maintaining the weld in a stable position, the risks associated with operator fatigue and poor ergonomics are minimized. This leads to a more focused work environment, reducing errors and improving workplace safety.
Selecting and Maintaining Your Welding Positioner
Choosing the right welding positioner is crucial for maximizing its benefits. Considerations include:
– **Specifications of the Workpiece**: Assess the size, weight, and shape of workpieces to determine the appropriate positioner type.
– **Purpose**: Identify whether the welding tasks require simple circumferential welds or more complex multi-axis processing.
– **Level of Automation**: Determine if manual handling is sufficient or if a fully automated setup is necessary due to high production volumes.
– **Space Consideration**: Ensure the workspace can accommodate the positioner and allow for operational movement.
While manual positioning methods may seem cost-effective, they often introduce risks and inefficiencies. In contrast, rotary positioners enhance productivity, reduce labor costs, and improve overall safety.
To ensure the longevity and reliability of a welding positioner, regular maintenance is essential. Operators should incorporate daily checks for loose hardware and wear, weekly lubrication of operational components, and monthly inspections of connections and terminals. Engaging a professional technician for annual assessments can further prevent costly issues.
In conclusion, a welding positioner is not merely an accessory but an essential component of modern welding operations. Investing in a quality positioner can significantly enhance safety, productivity, and overall profitability. As the welding industry continues to advance, the integration of sophisticated equipment like welding positioners will remain critical to achieving high standards of precision and efficiency.
-

 Health3 months ago
Health3 months agoNeurologist Warns Excessive Use of Supplements Can Harm Brain
-

 Health3 months ago
Health3 months agoFiona Phillips’ Husband Shares Heartfelt Update on Her Alzheimer’s Journey
-

 Science1 month ago
Science1 month agoBrian Cox Addresses Claims of Alien Probe in 3I/ATLAS Discovery
-

 Science1 month ago
Science1 month agoNASA Investigates Unusual Comet 3I/ATLAS; New Findings Emerge
-

 Science1 month ago
Science1 month agoScientists Examine 3I/ATLAS: Alien Artifact or Cosmic Oddity?
-

 Science1 month ago
Science1 month agoNASA Investigates Speedy Object 3I/ATLAS, Sparking Speculation
-

 Entertainment5 months ago
Entertainment5 months agoKerry Katona Discusses Future Baby Plans and Brian McFadden’s Wedding
-

 Entertainment4 months ago
Entertainment4 months agoEmmerdale Faces Tension as Dylan and April’s Lives Hang in the Balance
-

 World3 months ago
World3 months agoCole Palmer’s Cryptic Message to Kobbie Mainoo Following Loan Talks
-
 Science1 month ago
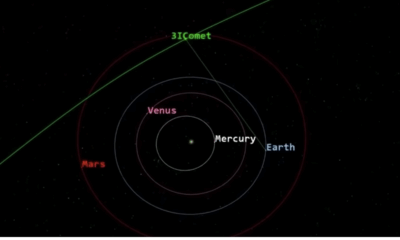
Science1 month agoNASA Scientists Explore Origins of 3I/ATLAS, a Fast-Moving Visitor
-

 Entertainment2 months ago
Entertainment2 months agoLewis Cope Addresses Accusations of Dance Training Advantage
-

 Entertainment3 months ago
Entertainment3 months agoMajor Cast Changes at Coronation Street: Exits and Returns in 2025