Health
Myosin II Boosts Immune Cell Speed with Temperature Changes
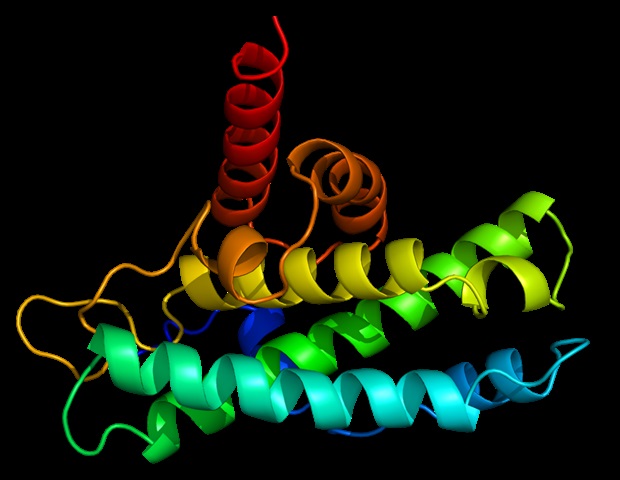
Temperature plays a critical role in regulating immune responses, a fact now confirmed by research from the University of Innsbruck. A team led by Stefan Wieser published findings in the journal Developmental Cell that reveal how the motor protein Myosin II influences the temperature sensitivity of immune cells, significantly accelerating their response during elevated body temperatures.
Wieser’s interest in the relationship between temperature and immune cell movement dates back nearly a decade. Through initial experiments at the Institute of Science and Technology Austria (ISTA), he observed that increasing the temperature from 20 °C to 40 °C markedly enhanced the motility of immune cells. At lower temperatures, the cells exhibited minimal movement, while at higher temperatures, their speed increased dramatically.
Despite the clear impact of temperature on immune cell behavior, the underlying molecular mechanisms remained largely unexplored until Wieser and his team began their systematic investigation. “It sounds surprising because the idea that immune cells react to temperature seems obvious,” he stated. “Yet there was no clue as to how this mechanism could work at the molecular level.”
Research conducted during Wieser’s tenure at the Institute of Photonic Sciences (ICFO) in Barcelona provided further insights. Utilizing a custom-built thermo-microscope, the team studied temperature sensitivity in various organisms, including zebrafish and mice, alongside cell cultures.
Myosin II Drives Immune Response Acceleration
The recent study revealed that when temperatures rose from 25 °C to 37 °C and even 41 °C, various types of human leukocytes—such as T cells, macrophages, dendritic cells, and neutrophils—demonstrated a dramatic increase in migration speed. Some cells exhibited up to a tenfold increase in speed, drastically reducing the time it takes for these immune cells to reach lymphatic vessels.
Furthermore, leukocytes responded almost instantaneously to temperature changes, indicating a biophysical mechanism that operates faster than traditional gene-regulation processes. “This clearly pointed to a biophysical mechanism, faster than any gene-regulation process,” Wieser explained.
By employing advanced fluorescence microscopy with precise temperature control at the single-cell level, the team identified Myosin II as the key driver behind this accelerated immune response. This motor protein is known for its critical roles in cell motility, division, and muscle contraction. As temperatures rise above 37 °C, Myosin II’s ability to generate mechanical force through ATP increases, enabling immune cells to move more rapidly.
Implications for Future Research
Wieser emphasized the importance of these findings, stating, “Our study shows that temperature is a crucial physiological control parameter that autonomously modulates both speed and morphological dynamics at the single-cell level in warm- and cold-blooded species alike.”
This research opens new avenues for exploration in both physiology and immunology. The implications of temperature on immune response efficiency could lead to advancements in understanding immune system behaviors during fever and other temperature-related conditions.
The full findings are documented in the article by Wieser and co-author Verena Ruprecht, titled “Myosin II regulates cellular thermo-adaptability and the efficiency of immune responses,” published in Developmental Cell.
-

 Health2 months ago
Health2 months agoNeurologist Warns Excessive Use of Supplements Can Harm Brain
-

 Health2 months ago
Health2 months agoFiona Phillips’ Husband Shares Heartfelt Update on Her Alzheimer’s Journey
-

 Science2 weeks ago
Science2 weeks agoBrian Cox Addresses Claims of Alien Probe in 3I/ATLAS Discovery
-

 Science2 weeks ago
Science2 weeks agoNASA Investigates Unusual Comet 3I/ATLAS; New Findings Emerge
-

 Science2 weeks ago
Science2 weeks agoScientists Examine 3I/ATLAS: Alien Artifact or Cosmic Oddity?
-

 Entertainment4 months ago
Entertainment4 months agoKerry Katona Discusses Future Baby Plans and Brian McFadden’s Wedding
-

 Science1 week ago
Science1 week agoNASA Investigates Speedy Object 3I/ATLAS, Sparking Speculation
-

 World2 months ago
World2 months agoCole Palmer’s Cryptic Message to Kobbie Mainoo Following Loan Talks
-

 Entertainment3 months ago
Entertainment3 months agoEmmerdale Faces Tension as Dylan and April’s Lives Hang in the Balance
-
 Science1 week ago
Science1 week agoNASA Scientists Explore Origins of 3I/ATLAS, a Fast-Moving Visitor
-

 Entertainment4 months ago
Entertainment4 months agoLove Island Star Toni Laite’s Mother Expresses Disappointment Over Coupling Decision
-

 Entertainment2 months ago
Entertainment2 months agoMajor Cast Changes at Coronation Street: Exits and Returns in 2025









