Science
New Findings Highlight SF6 Gas Emissions’ Climate Impact in Germany

Recent measurements have revealed that emissions of sulfur hexafluoride (SF6) in Germany are significantly more harmful to the climate than previously understood. SF6 is a gas that is chemically stable, colorless, odorless, and non-toxic. It is primarily utilized as an insulating and protective gas in electrical switchgear used in medium- and high-voltage engineering.
In addition to its current applications, SF6 was formerly employed in Germany for insulating soundproof windows and as a filling gas in sports shoes. However, the latter use was banned in 2006 due to environmental concerns.
Studies indicate that SF6 is approximately 24,000 times more potent as a greenhouse gas than carbon dioxide (CO2). This extraordinary impact on global warming has raised alarms among environmentalists and policymakers alike.
The significance of these findings cannot be understated, especially as global efforts to mitigate climate change become increasingly urgent. According to the German Federal Environment Agency, the volume of SF6 emissions has been closely monitored, but the latest data suggests that actual emissions may be higher than reported. The agency emphasizes the need for more stringent regulations and effective alternatives to SF6 in order to reduce its environmental footprint.
In the world of electrical engineering, SF6 has long been regarded as the preferred choice for insulation due to its superior properties. Its ability to withstand high voltages and prevent electrical arcs has made it indispensable in various applications. However, the growing awareness of its environmental impact is prompting engineers and manufacturers to explore alternative solutions.
As countries globally commit to reducing greenhouse gas emissions, the spotlight on SF6 presents both challenges and opportunities. Leading companies in the electrical sector are beginning to invest in research and development of alternative insulating gases that could replace SF6 in the near future.
The recent findings underscore the urgency for a comprehensive approach to addressing the climate crisis. With SF6 emissions contributing to a significant increase in global warming potential, stakeholders across industries must collaborate to identify sustainable practices and technologies.
In conclusion, while SF6 has played a crucial role in advancing electrical engineering, its environmental implications cannot be ignored. As Germany and the world strive to meet ambitious climate goals, the transition away from SF6 will be pivotal in shaping a sustainable future.
-

 Health3 months ago
Health3 months agoNeurologist Warns Excessive Use of Supplements Can Harm Brain
-

 Health3 months ago
Health3 months agoFiona Phillips’ Husband Shares Heartfelt Update on Her Alzheimer’s Journey
-

 Science2 months ago
Science2 months agoBrian Cox Addresses Claims of Alien Probe in 3I/ATLAS Discovery
-

 Science2 months ago
Science2 months agoNASA Investigates Unusual Comet 3I/ATLAS; New Findings Emerge
-

 Science1 month ago
Science1 month agoScientists Examine 3I/ATLAS: Alien Artifact or Cosmic Oddity?
-

 Entertainment5 months ago
Entertainment5 months agoKerry Katona Discusses Future Baby Plans and Brian McFadden’s Wedding
-

 Science1 month ago
Science1 month agoNASA Investigates Speedy Object 3I/ATLAS, Sparking Speculation
-

 Entertainment4 months ago
Entertainment4 months agoEmmerdale Faces Tension as Dylan and April’s Lives Hang in the Balance
-

 World3 months ago
World3 months agoCole Palmer’s Cryptic Message to Kobbie Mainoo Following Loan Talks
-
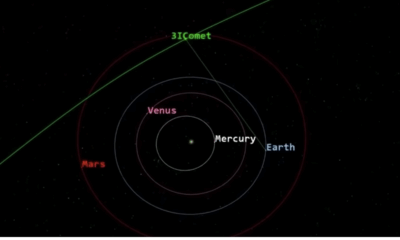
 Science1 month ago
Science1 month agoNASA Scientists Explore Origins of 3I/ATLAS, a Fast-Moving Visitor
-

 Entertainment2 months ago
Entertainment2 months agoLewis Cope Addresses Accusations of Dance Training Advantage
-

 Entertainment3 months ago
Entertainment3 months agoMajor Cast Changes at Coronation Street: Exits and Returns in 2025