Health
New Study Reveals Ticks’ Microbiota Influence Disease Transmission
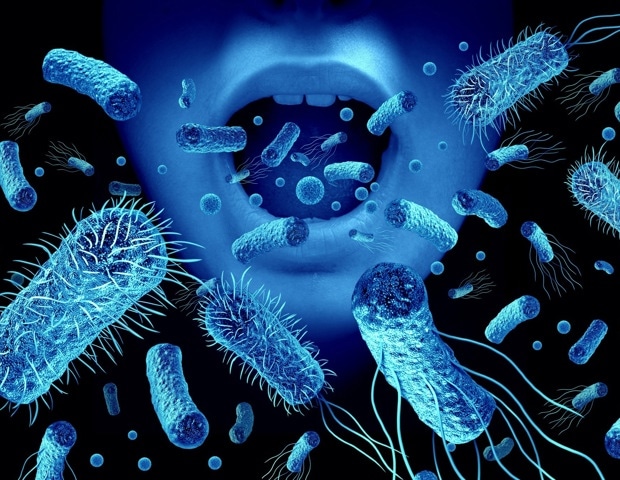
A recent publication in the Zoonoses journal sheds light on the complex relationship between ticks and their microbiota, emphasizing their role in disease transmission. Researchers are increasingly focused on ticks due to their capacity to carry pathogens that can infect both humans and animals. The review, authored by Chang, X. and colleagues, explores how the intricate interactions between ticks and their endosymbionts affect disease dynamics.
The study examines the epidemiology of tick-borne diseases and the composition of tick microbiota. These microorganisms play a significant role in the developmental processes and reproductive success of ticks. Understanding these relationships offers insights into the potential for ticks to act as vectors for various diseases.
Microbiota’s Role in Disease Transmission
The paper highlights that the presence of specific microorganisms within ticks can enhance their ability to transmit pathogens. By reviewing existing literature, the authors detail how certain symbiotic relationships not only aid in tick survival but can also influence the vector’s capacity to spread diseases like Lyme disease and Rocky Mountain spotted fever.
Moreover, the authors discuss the significance of tick immunity in maintaining gut homeostasis. A healthy gut microbiome supports the overall health of ticks, which is crucial for their role in disease ecology. This aspect of tick biology is essential for understanding how ticks can control pathogen loads and influence disease spread.
Strategies for Controlling Tick-Borne Diseases
The review also offers potential strategies for managing tick-borne diseases by leveraging these symbiotic relationships. By manipulating the tick microbiota, researchers could develop new methods for preventing the transmission of pathogens. This approach could lead to breakthroughs in controlling diseases that pose a significant threat to public health.
The findings presented in this article by Chang, X. et al. underscore the importance of further research into tick microbiota and their impact on disease transmission. As the landscape of tick-borne diseases continues to evolve, understanding these microbial relationships will be crucial for developing effective intervention strategies.
The comprehensive review is part of ongoing efforts to address the challenges posed by tick-borne diseases and is set to influence future research directions in this vital area of public health. For those interested in the intricate dynamics of ticks and pathogens, this study is a significant contribution to the field.
The full article, titled “Roles of Tick Symbiotic Microorganisms in Pathogen Transmission,” is accessible through Compuscript Ltd and can be found at doi.org/10.15212/ZOONOSES-2024-0067, published in 2025.
-

 Health3 months ago
Health3 months agoNeurologist Warns Excessive Use of Supplements Can Harm Brain
-

 Health3 months ago
Health3 months agoFiona Phillips’ Husband Shares Heartfelt Update on Her Alzheimer’s Journey
-

 Science1 month ago
Science1 month agoBrian Cox Addresses Claims of Alien Probe in 3I/ATLAS Discovery
-

 Science1 month ago
Science1 month agoNASA Investigates Unusual Comet 3I/ATLAS; New Findings Emerge
-

 Science4 weeks ago
Science4 weeks agoScientists Examine 3I/ATLAS: Alien Artifact or Cosmic Oddity?
-

 Entertainment4 months ago
Entertainment4 months agoKerry Katona Discusses Future Baby Plans and Brian McFadden’s Wedding
-

 Science4 weeks ago
Science4 weeks agoNASA Investigates Speedy Object 3I/ATLAS, Sparking Speculation
-

 Entertainment4 months ago
Entertainment4 months agoEmmerdale Faces Tension as Dylan and April’s Lives Hang in the Balance
-

 World3 months ago
World3 months agoCole Palmer’s Cryptic Message to Kobbie Mainoo Following Loan Talks
-
 Science4 weeks ago
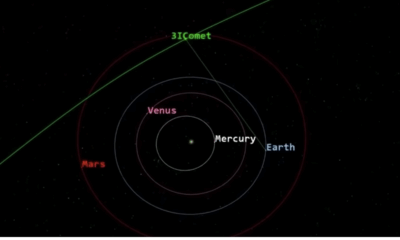
Science4 weeks agoNASA Scientists Explore Origins of 3I/ATLAS, a Fast-Moving Visitor
-

 Entertainment4 months ago
Entertainment4 months agoLove Island Star Toni Laite’s Mother Expresses Disappointment Over Coupling Decision
-

 Entertainment3 months ago
Entertainment3 months agoMajor Cast Changes at Coronation Street: Exits and Returns in 2025









