Science
Robotic Gyroscopic Backpack Enhances Balance for Ataxia Patients
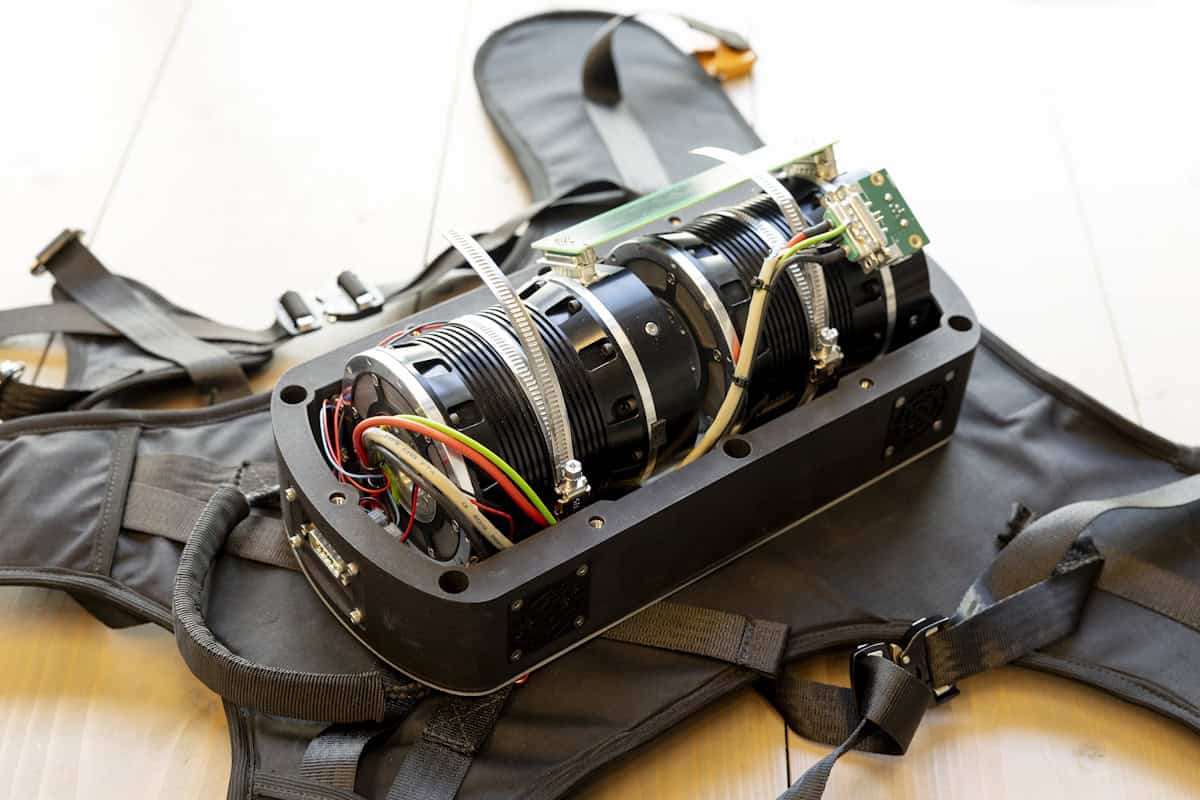

A new robotic backpack, known as the GyroPack, has shown promise in improving balance for individuals suffering from severe movement disorders, particularly ataxia. This innovative device utilizes gyroscopic technology similar to that found in satellites to stabilize the wearer’s torso and potentially reduce reliance on mobility aids like walkers.
Developed over a decade by a collaborative team from the Radboud University Medical Centre, Delft University of Technology (TU Delft), and Erasmus Medical Centre, the GyroPack was recently tested in a study involving 14 adults diagnosed with degenerative ataxia. The findings, published in the journal npj Robotics, indicate that the device significantly enhances balance performance during various exercises, including standing still and walking.
Understanding Ataxia and the GyroPack’s Functionality
Ataxia encompasses a range of neurological disorders that lead to progressive impairment of coordination and balance. Symptoms can affect individuals of all ages, making daily activities challenging and often necessitating the use of cumbersome mobility aids. The 6 kg GyroPack is designed to address these issues by incorporating two control moment gyroscopes (CMGs). These gyroscopes maintain orientation and dampen unwanted movements of the torso.
According to Jorik Nonnekes, the lead researcher at Radboud UMC, the gyroscopes generate a torque that counteracts the body’s unintended motions. “The gimbal motor’s orientation change, combined with the flywheels’ angular momentum, produces a free moment that helps stabilize the upper body,” Nonnekes explained. This approach aims to make it easier for users to maintain balance, drawing on techniques that have proven effective for both healthy individuals and those recovering from strokes.
Performance Assessment and Future Developments
In the recent study, participants engaged in five specific tasks to measure balance and stability. These included standing with feet together, walking on a treadmill, and turning in place. The GyroPack was assessed in two operational modes: one providing active assistance and another functioning as a placebo, where the device offered no real support.
The researchers reported that when the GyroPack was fully operational, it increased the average standing time of the users and reduced variability in trunk angular velocity, indicative of improved gait stability. Notably, even the placebo mode showed benefits, suggesting that the added weight of the backpack might contribute to better stabilization or perhaps trigger a placebo effect.
Despite these promising results, Nonnekes noted that the current version is not yet ready for everyday use. Future iterations of the GyroPack will focus on reducing weight and noise levels, making it more practical for daily life. “Our goal is to enable individuals with ataxia to engage more freely in social activities without the need for bulky walkers,” he stated. Such advancements could significantly enhance their mobility and overall quality of life.
The GyroPack represents a significant step forward in assistive technology for individuals with movement disorders, showcasing the intersection of innovative engineering and compassionate healthcare. As development continues, the potential for broader applications of this technology could pave the way for improved independence for many.
-

 Health3 months ago
Health3 months agoNeurologist Warns Excessive Use of Supplements Can Harm Brain
-

 Health3 months ago
Health3 months agoFiona Phillips’ Husband Shares Heartfelt Update on Her Alzheimer’s Journey
-

 Science2 months ago
Science2 months agoBrian Cox Addresses Claims of Alien Probe in 3I/ATLAS Discovery
-

 Science2 months ago
Science2 months agoNASA Investigates Unusual Comet 3I/ATLAS; New Findings Emerge
-

 Science1 month ago
Science1 month agoScientists Examine 3I/ATLAS: Alien Artifact or Cosmic Oddity?
-

 Entertainment5 months ago
Entertainment5 months agoKerry Katona Discusses Future Baby Plans and Brian McFadden’s Wedding
-

 Science1 month ago
Science1 month agoNASA Investigates Speedy Object 3I/ATLAS, Sparking Speculation
-

 Entertainment4 months ago
Entertainment4 months agoEmmerdale Faces Tension as Dylan and April’s Lives Hang in the Balance
-

 World3 months ago
World3 months agoCole Palmer’s Cryptic Message to Kobbie Mainoo Following Loan Talks
-
 Science1 month ago
Science1 month agoNASA Scientists Explore Origins of 3I/ATLAS, a Fast-Moving Visitor
-

 Entertainment2 months ago
Entertainment2 months agoLewis Cope Addresses Accusations of Dance Training Advantage
-

 Entertainment3 months ago
Entertainment3 months agoMajor Cast Changes at Coronation Street: Exits and Returns in 2025