Science
Ancient Skull Discovery Challenges Human Evolution Theories
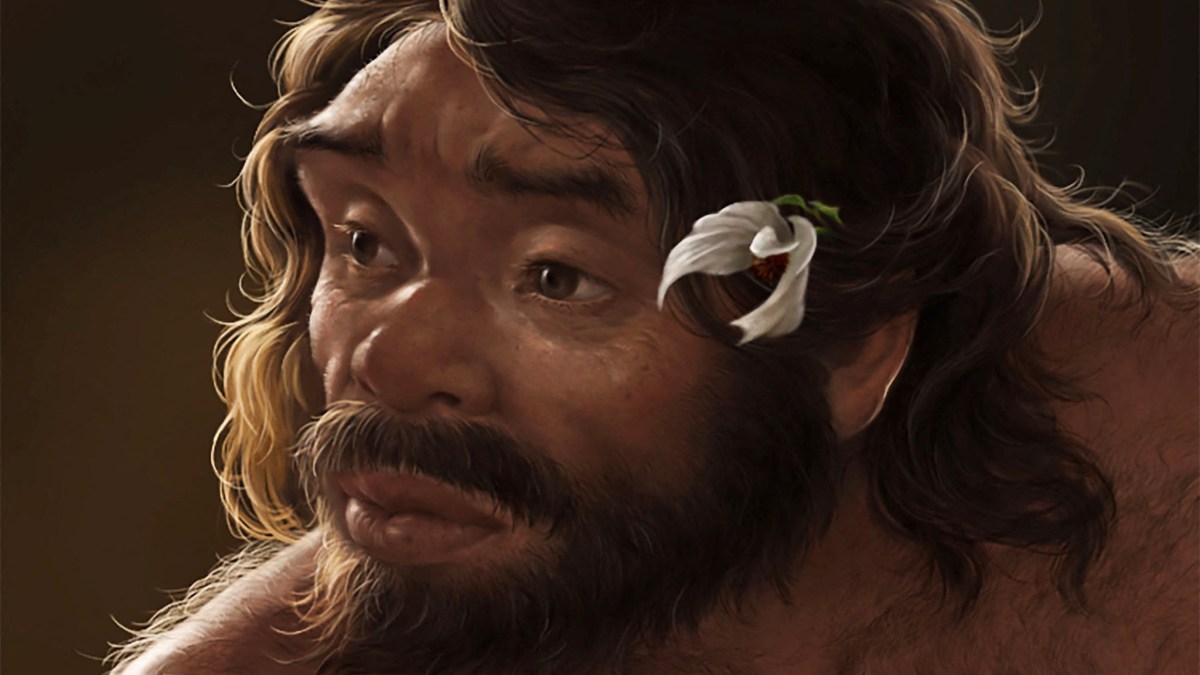

A skull discovered in China, known as Yunxian 2, is poised to reshape theories surrounding human evolution. This ancient find suggests that Homo sapiens may have emerged in Asia up to 400,000 years earlier than previously believed, challenging the long-held view that human evolution began in Africa.
Located in the Hunan province of China, the skull is estimated to be around 1 million years old. Researchers from a collaborative study, which includes contributions from Chinese archaeologists and international experts, published their findings in the prestigious Nature Journal. The implications of this discovery could significantly alter the understanding of human ancestry and migration patterns.
The Yunxian 2 skull displays distinct characteristics that align with early human traits. This discovery brings forth the possibility that Homo sapiens may have developed unique traits in different regions. The research team has emphasized that these findings do not discount the significance of Africa in human evolution but rather highlight a more complex narrative involving multiple locations.
The skull was found in a geological stratum containing other artifacts that suggest it may have belonged to a species that lived in a diverse ecosystem. The findings indicate that early humans were capable of adapting to various environments much earlier than previously thought. This adaptability could have implications for understanding how ancient populations spread across continents.
In light of these findings, the research team is calling for a reassessment of existing models of human evolution. They argue that if early human populations were present in Asia alongside those in Africa, then the timeline for human development requires significant revision.
The discovery of Yunxian 2 adds to a growing body of evidence that questions the singular narrative of human evolution centered on Africa. As researchers continue to explore this ancient skull, they hope to uncover more insights into the life and environment of early humans.
This research not only sheds light on the evolutionary history of our species but also raises questions about how migration patterns influenced the genetic diversity seen in modern humans. The implications of the Yunxian 2 find extend beyond academic interest; they touch on the fundamental aspects of what it means to be human.
As this story unfolds, further studies and excavations are expected to yield more information that could potentially rewrite parts of the human evolutionary timeline. The scientific community eagerly awaits the next chapters in this ongoing exploration of our origins.
-

 Health3 months ago
Health3 months agoNeurologist Warns Excessive Use of Supplements Can Harm Brain
-

 Health3 months ago
Health3 months agoFiona Phillips’ Husband Shares Heartfelt Update on Her Alzheimer’s Journey
-

 Science2 months ago
Science2 months agoBrian Cox Addresses Claims of Alien Probe in 3I/ATLAS Discovery
-

 Science2 months ago
Science2 months agoNASA Investigates Unusual Comet 3I/ATLAS; New Findings Emerge
-

 Science1 month ago
Science1 month agoScientists Examine 3I/ATLAS: Alien Artifact or Cosmic Oddity?
-

 Entertainment5 months ago
Entertainment5 months agoKerry Katona Discusses Future Baby Plans and Brian McFadden’s Wedding
-

 Science1 month ago
Science1 month agoNASA Investigates Speedy Object 3I/ATLAS, Sparking Speculation
-

 Entertainment4 months ago
Entertainment4 months agoEmmerdale Faces Tension as Dylan and April’s Lives Hang in the Balance
-

 World3 months ago
World3 months agoCole Palmer’s Cryptic Message to Kobbie Mainoo Following Loan Talks
-
 Science1 month ago
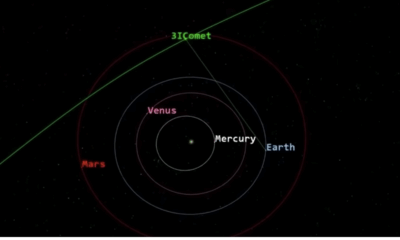
Science1 month agoNASA Scientists Explore Origins of 3I/ATLAS, a Fast-Moving Visitor
-

 Entertainment2 months ago
Entertainment2 months agoLewis Cope Addresses Accusations of Dance Training Advantage
-

 Entertainment3 months ago
Entertainment3 months agoMajor Cast Changes at Coronation Street: Exits and Returns in 2025