Health
Researchers Identify New Genetic Mutation in Invasive Strep Bacteria

A team of researchers from The University of Osaka has discovered a novel genetic mutation in Streptococcus pyogenes, a bacterium responsible for strep throat, which is significantly associated with severe invasive infections. This mutation affects a ferric ion transporter within the bacterium, which in turn weakens its growth in human blood. Unique to Japanese strains, this finding indicates a previously unknown pathogenic mechanism that could pave the way for new treatment strategies.
The study comes at a critical time, as cases of invasive strep infections in Japan surged in 2024, raising alarms among health officials. The high mortality rate associated with severe infections underscores the urgent need for enhanced understanding and new therapeutic options.
Comprehensive Genomic Analysis Reveals Key Findings
The researchers conducted an extensive analysis of 666 strains of S. pyogenes, comprising 311 samples from Japan and 355 from various other countries. By employing cutting-edge pangenome-wide association studies, the team uncovered numerous genetic changes linked to the bacterium’s ability to cause severe infections. Among these was a previously unseen mutation affecting a gene responsible for the bacterium’s iron acquisition, a critical nutrient for its survival.
Interestingly, the study revealed that many genes previously thought to contribute to serious illness were actually common among less harmful strains. This suggests a paradigm shift in understanding how some strains become more virulent; it may not solely depend on acquiring harmful genes but could also involve the loss of genes that otherwise suppress their pathogenic potential.
Dr. Masayuki Ono, the lead author of the study and an assistant professor at the Graduate School of Dentistry at The University of Osaka, emphasized the significance of their findings. He stated, “This research significantly advances our understanding of severe invasive strep, especially within the Japanese population.” The comprehensive genomic analysis, which utilized advanced supercomputer techniques and experimental validation, offers a promising pathway for developing therapies that target the mutated iron transporter.
Implications for Future Research and Treatment
The implications of this research extend beyond Japan. The pangenome-wide approach showcased the potential of large-scale genomic analyses to unravel complex disease mechanisms. This methodology could serve as a valuable tool for future research into other infectious diseases, enhancing our overall understanding of microbial pathogenesis.
The findings have been published in the journal eLife, contributing to the growing body of knowledge surrounding S. pyogenes and its invasive capabilities. As researchers continue to explore the intricacies of this bacterium, the hope is that new preventive measures and treatments will emerge, ultimately reducing the burden of severe invasive infections worldwide.
The study represents a significant step in infectious disease research, highlighting the importance of ongoing surveillance and genetic analysis to combat emerging health threats.
-

 Health3 months ago
Health3 months agoNeurologist Warns Excessive Use of Supplements Can Harm Brain
-

 Health3 months ago
Health3 months agoFiona Phillips’ Husband Shares Heartfelt Update on Her Alzheimer’s Journey
-

 Science1 month ago
Science1 month agoBrian Cox Addresses Claims of Alien Probe in 3I/ATLAS Discovery
-

 Science1 month ago
Science1 month agoNASA Investigates Unusual Comet 3I/ATLAS; New Findings Emerge
-

 Science4 weeks ago
Science4 weeks agoScientists Examine 3I/ATLAS: Alien Artifact or Cosmic Oddity?
-

 Entertainment4 months ago
Entertainment4 months agoKerry Katona Discusses Future Baby Plans and Brian McFadden’s Wedding
-

 Science4 weeks ago
Science4 weeks agoNASA Investigates Speedy Object 3I/ATLAS, Sparking Speculation
-

 Entertainment4 months ago
Entertainment4 months agoEmmerdale Faces Tension as Dylan and April’s Lives Hang in the Balance
-

 World3 months ago
World3 months agoCole Palmer’s Cryptic Message to Kobbie Mainoo Following Loan Talks
-
 Science4 weeks ago
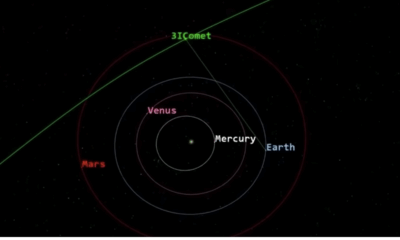
Science4 weeks agoNASA Scientists Explore Origins of 3I/ATLAS, a Fast-Moving Visitor
-

 Entertainment4 months ago
Entertainment4 months agoLove Island Star Toni Laite’s Mother Expresses Disappointment Over Coupling Decision
-

 Entertainment3 months ago
Entertainment3 months agoMajor Cast Changes at Coronation Street: Exits and Returns in 2025









