Health
Understand HPV: The Common Virus Linked to Cancer Risks
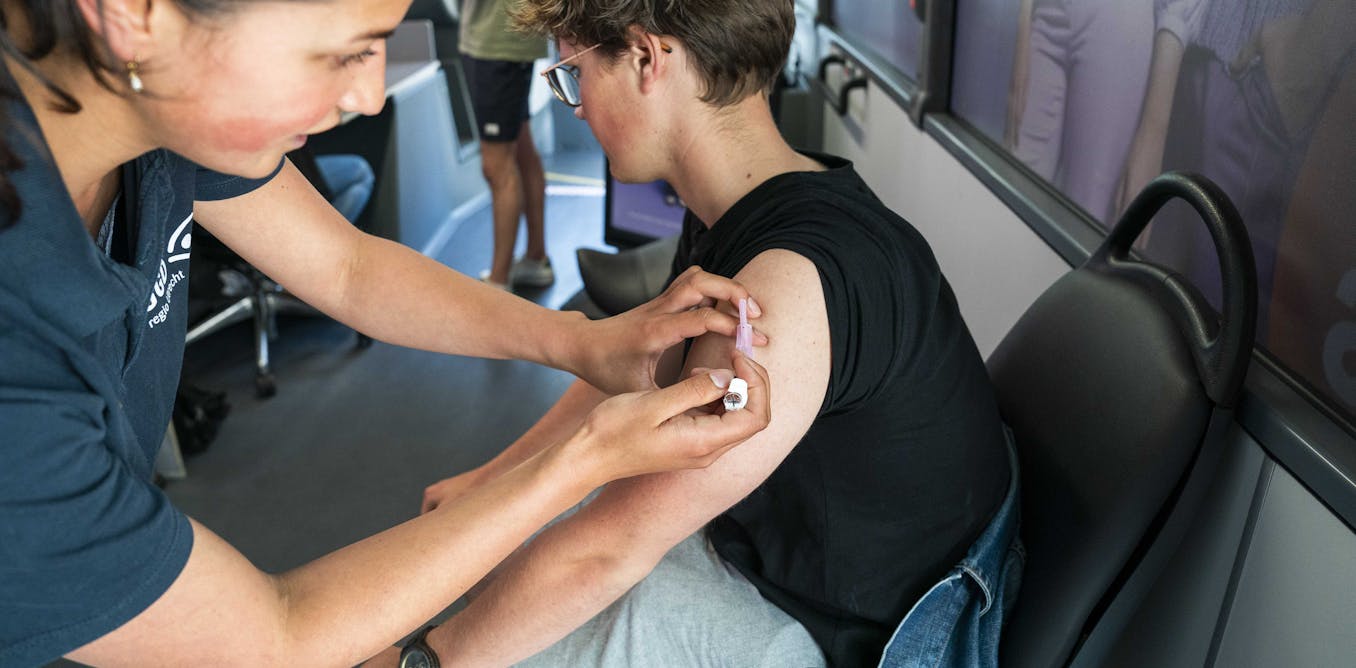
Human papillomavirus (HPV) is a widely prevalent virus that affects a significant portion of the population, with estimates suggesting that up to 80% of individuals will encounter it at some point in their lives. Understanding this virus is crucial, especially since certain strains of HPV are linked to various cancers. With over 200 identified types, HPV is one of the most diverse viral families, making it essential for public awareness to distinguish between its low-risk and high-risk strains.
Understanding HPV and Its Risks
Many strains of HPV are low risk and cause minor symptoms such as benign warts. For example, HPV types 1, 2, and 4 are commonly associated with skin warts. Others, like HPV 6 and 11, lead to genital warts—small growths that can appear on the genitals or around the anus. While treatments exist to remove these visible warts, they do not eliminate the virus itself, which means it can still be transmitted until the body clears it.
The more concerning strains, particularly HPV 16 and 18, are classified as high-risk due to their established links to cancer. These types can integrate into human cells and damage DNA, disrupting normal cellular growth and division. Persistent infections with these strains elevate the risk of developing cancers not only of the cervix but also of the vulva, vagina, anus, penis, mouth, and throat.
Five Essential Facts About HPV
1. **Broad Cancer Associations**: While cervical cancer is the most recognized malignancy associated with HPV, it also contributes to various other cancers. This broad spectrum of risk underscores the importance of the HPV vaccine, which is recommended for all sexes.
2. **Asymptomatic Transmission**: Individuals infected with HPV can transmit the virus without exhibiting any symptoms or having visible genital warts. The virus can remain on the skin for months, allowing transmission through skin contact before symptoms emerge. This highlights the importance of condom use even after warts have cleared.
3. **Transmission Routes**: HPV does not solely spread through vaginal or anal sex; oral sex can also lead to infections that may result in mouth and throat cancers. Studies indicate that oral sex is a significant behavioral risk factor for these cancers, emphasizing the need for protective measures, including the use of condoms.
4. **Limitations of Condoms**: While condoms can reduce the risk of HPV transmission, they are not entirely effective. Uncovered skin can still harbor the virus, meaning many sexually active individuals will likely encounter some strain of HPV during their lives.
5. **Continued Screening for Vaccinated Individuals**: Current HPV vaccines target the main high-risk strains but cannot prevent all cancer-causing strains or treat existing infections. Consequently, women aged 25 to 64 are still advised to undergo cervical screening every five years, regardless of vaccination status.
The uptake of the HPV vaccine has seen declines in some regions, partly due to disruptions caused by the COVID-19 pandemic and misinformation surrounding vaccine safety and efficacy. Many individuals are still unaware of HPV’s connection to various cancers, as well as the necessity to vaccinate boys alongside girls.
The World Health Organization (WHO) has set a target for 2030 to fully vaccinate 90% of girls by age 15. Currently, only about 48% of girls worldwide are fully vaccinated, indicating a pressing need for increased public awareness and education.
Despite the potential risks associated with certain strains of HPV, it is crucial not to instill fear regarding sexual activity. The HPV vaccine provides protection not only for the individual but also for future partners. By staying informed and taking preventive measures, individuals can effectively reduce the impact of this common virus and foster a healthier community.
Dan Baumgardt, the author of this article, does not hold any affiliations or receive funding from any organization that would benefit from this information, aside from his academic position.
-

 Health3 months ago
Health3 months agoNeurologist Warns Excessive Use of Supplements Can Harm Brain
-

 Health3 months ago
Health3 months agoFiona Phillips’ Husband Shares Heartfelt Update on Her Alzheimer’s Journey
-

 Science1 month ago
Science1 month agoBrian Cox Addresses Claims of Alien Probe in 3I/ATLAS Discovery
-

 Science1 month ago
Science1 month agoNASA Investigates Unusual Comet 3I/ATLAS; New Findings Emerge
-

 Science4 weeks ago
Science4 weeks agoScientists Examine 3I/ATLAS: Alien Artifact or Cosmic Oddity?
-

 Entertainment4 months ago
Entertainment4 months agoKerry Katona Discusses Future Baby Plans and Brian McFadden’s Wedding
-

 Science4 weeks ago
Science4 weeks agoNASA Investigates Speedy Object 3I/ATLAS, Sparking Speculation
-

 Entertainment4 months ago
Entertainment4 months agoEmmerdale Faces Tension as Dylan and April’s Lives Hang in the Balance
-

 World3 months ago
World3 months agoCole Palmer’s Cryptic Message to Kobbie Mainoo Following Loan Talks
-
 Science4 weeks ago
Science4 weeks agoNASA Scientists Explore Origins of 3I/ATLAS, a Fast-Moving Visitor
-

 Entertainment4 months ago
Entertainment4 months agoLove Island Star Toni Laite’s Mother Expresses Disappointment Over Coupling Decision
-

 Entertainment3 months ago
Entertainment3 months agoMajor Cast Changes at Coronation Street: Exits and Returns in 2025









