Health
Understanding Adult ADHD: Diagnosis and Its Challenges
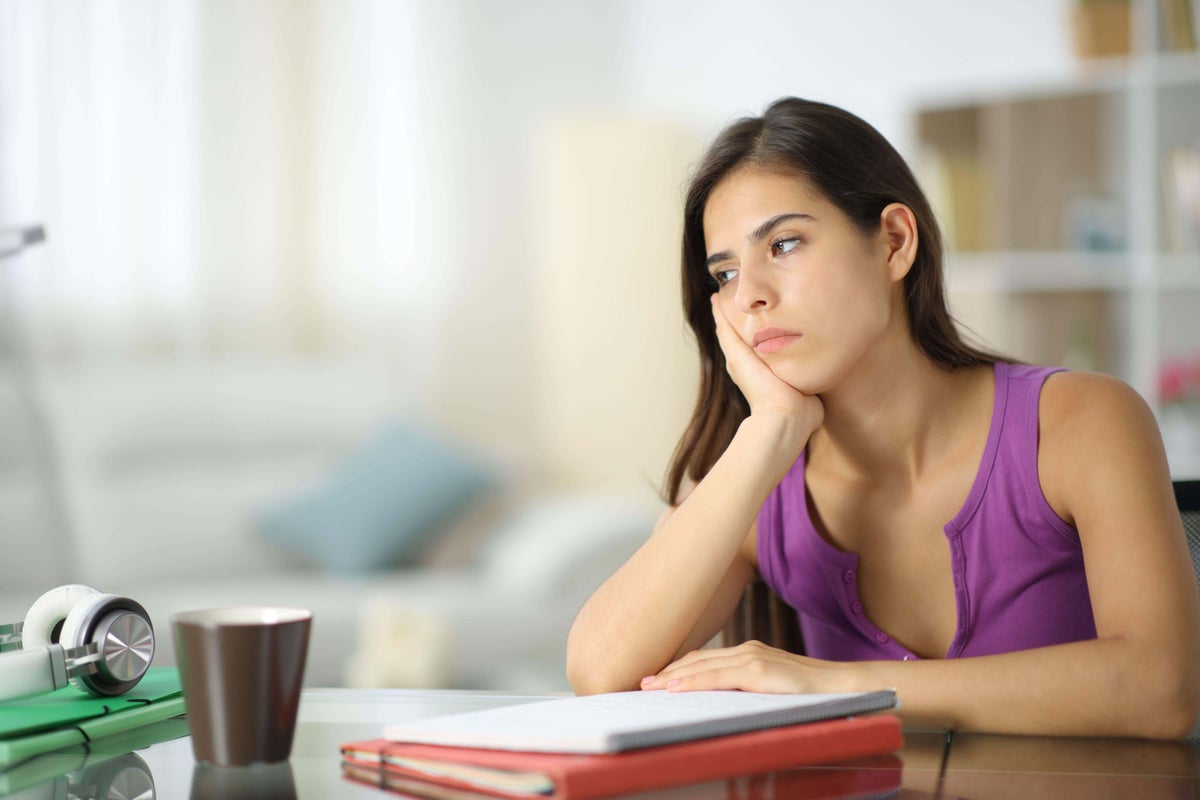

Attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) affects approximately 2.5% of adults and 7% of children globally. This neurodevelopmental condition can lead to significant difficulties with attention, impulsivity, and hyperactivity. If left unrecognized and untreated, ADHD can severely impact educational and work achievements, as well as social and emotional wellbeing. It also increases the risk of serious accidents, mental illness, and substance abuse.
A recent article in the Medical Journal of Australia emphasizes that while effective treatments exist, many individuals face challenges in accessing formal diagnoses and care. The article raises concerns about the proliferation of online ADHD “tests” on social media platforms, which are often sponsored by private clinics. These tests can direct users to paid assessments, leading to apprehension about the potential for over-diagnosis.
Defining ADHD Diagnosis
The diagnosis of ADHD is primarily based on functional impairment, which refers to how symptoms affect a person’s daily life. Reports indicate that some clinics in Australia charge several thousand dollars for a brief online assessment. Such assessments often do not adhere to evidence-based guidelines, which complicates the accurate identification of ADHD.
A critical requirement for diagnosing ADHD is the presence of symptoms that cause functional impairment. A diagnosis should not be made solely based on the number of symptoms present; rather, the impact of those symptoms on daily activities must be evaluated. A comprehensive assessment is essential and typically includes a clinical interview that examines both the current and past presence of the 18 core ADHD symptoms.
While tools such as the Weiss Functional Impairment Rating Scale and the World Health Organization Disability Assessment Schedule can assist in the evaluation process, they should not replace thorough interviews. A detailed assessment also involves examining an individual’s mental and physical health history, developmental background, and any family history of mental illness or substance abuse.
Moreover, it is crucial for clinicians to gather information from individuals who know the patient well to provide insight into their childhood and current functioning. This approach helps ensure a more accurate diagnosis rather than a simple yes-or-no assessment.
The Challenge of Defining Impairment
Diagnostic manuals do not provide a standardized definition of what constitutes significant impairment for an ADHD diagnosis. This lack of clarity has led to concerns from some experts about the risk of over-diagnosis. The diverse nature of ADHD’s impact means that creating a comprehensive list of valid impairments is challenging, as individuals may experience different difficulties.
For example, a person may excel in certain areas such as work or academics, yet still struggle significantly in other aspects of life. A person with ADHD might perform well professionally but feel exhausted by the end of the day, preventing them from engaging in personal activities. It is essential for clinicians to explore these nuances to differentiate between genuine impairments and those that may not substantially affect daily functioning.
Research indicates that common themes associated with ADHD symptoms include challenges in time management, organization, and maintaining attention. Some individuals manage to cope with their symptoms through support systems or personal strategies, complicating the assessment process. Clinicians must thoughtfully evaluate whether these adaptations constitute genuine impairments.
Despite the complexities involved, assessing impairments associated with ADHD is a skill that can be developed. Experienced clinicians can effectively evaluate functional impacts, often arriving at similar conclusions regarding diagnoses. However, a significant gap remains in the training of healthcare professionals in ADHD assessment practices.
To improve diagnostic accuracy and reduce the likelihood of missed or misdiagnoses, enhanced training on ADHD for healthcare professionals is crucial. Without such changes, many individuals may continue to face barriers in receiving appropriate care and support for their conditions.
-

 Health3 months ago
Health3 months agoNeurologist Warns Excessive Use of Supplements Can Harm Brain
-

 Health3 months ago
Health3 months agoFiona Phillips’ Husband Shares Heartfelt Update on Her Alzheimer’s Journey
-

 Science2 months ago
Science2 months agoBrian Cox Addresses Claims of Alien Probe in 3I/ATLAS Discovery
-

 Science2 months ago
Science2 months agoNASA Investigates Unusual Comet 3I/ATLAS; New Findings Emerge
-

 Science1 month ago
Science1 month agoScientists Examine 3I/ATLAS: Alien Artifact or Cosmic Oddity?
-

 Entertainment5 months ago
Entertainment5 months agoKerry Katona Discusses Future Baby Plans and Brian McFadden’s Wedding
-

 Science1 month ago
Science1 month agoNASA Investigates Speedy Object 3I/ATLAS, Sparking Speculation
-

 Entertainment4 months ago
Entertainment4 months agoEmmerdale Faces Tension as Dylan and April’s Lives Hang in the Balance
-

 World3 months ago
World3 months agoCole Palmer’s Cryptic Message to Kobbie Mainoo Following Loan Talks
-
 Science1 month ago
Science1 month agoNASA Scientists Explore Origins of 3I/ATLAS, a Fast-Moving Visitor
-

 Entertainment2 months ago
Entertainment2 months agoLewis Cope Addresses Accusations of Dance Training Advantage
-

 Entertainment3 months ago
Entertainment3 months agoMajor Cast Changes at Coronation Street: Exits and Returns in 2025