Science
AI Algorithms Revolutionize Contouring of Brain Metastases
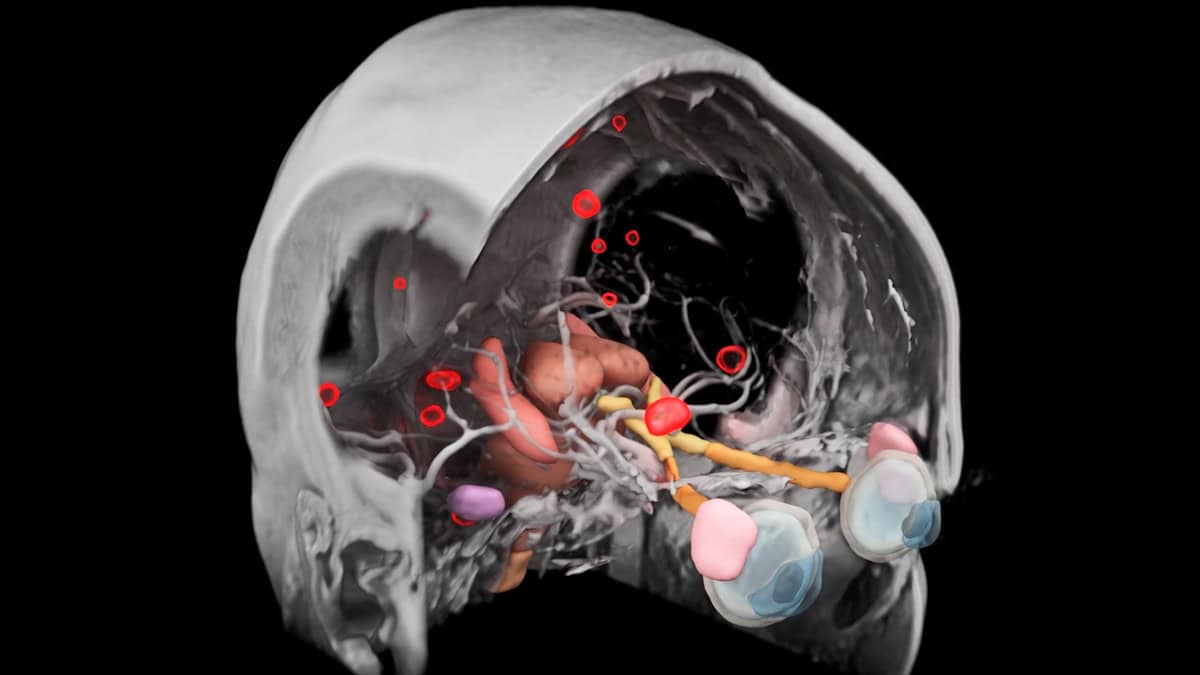
Advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) are transforming the treatment of brain metastases, cancerous lesions that spread from other parts of the body. A new AI-powered software developed by Siemens Healthineers enhances the accuracy and speed of contouring these lesions, a crucial step in stereotactic radiotherapy (SRS). This precision technique administers high doses of radiation directly to individual lesions, offering significant benefits over traditional whole-brain irradiation.
The challenge of accurately identifying and delineating multiple brain metastases is considerable. According to Evrim Tezcanli, a professor of radiation oncology at Acibadem Atasehir Hospital in Turkey, “Very small lesions, particularly those under 0.1 cc, can easily be missed by untrained eyes.” Larger lesions present their own difficulties, as precise contouring is necessary to avoid unnecessary radiation exposure to healthy brain tissue.
To tackle these issues, Siemens Healthineers integrated advanced deep-learning algorithms into their syngo.via RT Image Suite and AI-Rad Companion Organs RT packages. This software quickly analyzes MRI images, automatically contouring and labeling metastatic lesions while also outlining critical surrounding organs, such as the brainstem and optic structures.
Research Findings Support AI Integration
Tezcanli and her team conducted a comprehensive study to evaluate the effectiveness of the AI software in contouring brain metastases. They compared its performance against two experienced radiation oncologists who manually contoured all lesions from contrast-enhanced MRI scans. The study involved data from 10 patients, each presenting between three and 17 brain metastases, with a total of 82 lesions.
The findings were promising. Tezcanli noted that the contours produced by the software showed a strong agreement with those of the experienced oncologists, particularly for lesions larger than 0.1 cc. “In terms of geometric similarity, the AI-generated boundaries were well within our clinically acceptable levels,” she stated. The study recorded a medium Dice similarity coefficient of 0.83, which improved to 0.91 when excluding the smallest lesions.
In terms of efficiency, the AI software completed contouring for each patient in just one to two minutes, leading to an average workload reduction of 75%. In some cases, it saved over 30 minutes per patient. Tezcanli emphasized the importance of expert review, noting that while the AI tool greatly reduced the time spent on contouring, oncologists still needed to verify and adjust the contours, typically taking only three to four minutes for review.
Enhancing Patient Care and Treatment Efficiency
The implications of this technology extend beyond operational efficiency. By minimizing the time spent on manual contouring, physicians can dedicate more attention to patient care. The study used high-resolution post-contrast T1 MPRAGE sequences recorded on a 3 Tesla MRI scanner, enhancing lesion visibility and accuracy in treatment planning.
The AI software demonstrated an overall sensitivity of 94%, successfully identifying 77 of the 82 lesions. The five missed lesions were extremely small, within the range of 0.01 to 0.03 cc, which poses a challenge even for seasoned practitioners. Remarkably, the AI also identified three additional lesions that were initially overlooked, which were later confirmed as brain metastases.
While the AI tool showed an 8.5% false positive rate, identifying some vascular structures as metastases, Tezcanli remains optimistic. “We were very satisfied with the software’s ability to detect small lesions and find ones that we hadn’t detected,” she added.
The contours generated by the AI software are exported in DICOM RT Struct format, allowing seamless integration into treatment planning systems like HyperArc. This radiosurgery-specific module automates treatment planning and delivery, significantly streamlining the SRS process.
Tezcanli highlighted the rapid advancements in technology: “We are in an era where we are using the technology to have even same-day treatments.” With efficient AI contouring and planning, patients can potentially undergo treatment on the same day as their MRI scan, improving overall care and outcomes.
As the landscape of cancer treatment continues to evolve, the integration of AI in clinical practice is expected to expand. Tezcanli anticipates a growing reliance on SRS as the primary treatment modality for brain metastases, driven by the significant time savings and accuracy offered by AI tools. While the current version of the software is a significant step forward, she envisions further enhancements that could improve its sensitivity and specificity.
The team at Acibadem Atasehir Hospital is keen to incorporate this technology into their routine patient care, viewing it as a vital component of future treatments. The integration of AI into radiation oncology not only represents a leap in technological advancement but also offers the promise of better patient outcomes in the fight against cancer.
-

 Health3 months ago
Health3 months agoNeurologist Warns Excessive Use of Supplements Can Harm Brain
-

 Health3 months ago
Health3 months agoFiona Phillips’ Husband Shares Heartfelt Update on Her Alzheimer’s Journey
-

 Science2 months ago
Science2 months agoBrian Cox Addresses Claims of Alien Probe in 3I/ATLAS Discovery
-

 Science2 months ago
Science2 months agoNASA Investigates Unusual Comet 3I/ATLAS; New Findings Emerge
-

 Science1 month ago
Science1 month agoScientists Examine 3I/ATLAS: Alien Artifact or Cosmic Oddity?
-

 Entertainment5 months ago
Entertainment5 months agoKerry Katona Discusses Future Baby Plans and Brian McFadden’s Wedding
-

 Science1 month ago
Science1 month agoNASA Investigates Speedy Object 3I/ATLAS, Sparking Speculation
-

 Entertainment4 months ago
Entertainment4 months agoEmmerdale Faces Tension as Dylan and April’s Lives Hang in the Balance
-

 World3 months ago
World3 months agoCole Palmer’s Cryptic Message to Kobbie Mainoo Following Loan Talks
-
 Science1 month ago
Science1 month agoNASA Scientists Explore Origins of 3I/ATLAS, a Fast-Moving Visitor
-

 Entertainment2 months ago
Entertainment2 months agoLewis Cope Addresses Accusations of Dance Training Advantage
-

 Entertainment3 months ago
Entertainment3 months agoMajor Cast Changes at Coronation Street: Exits and Returns in 2025