Science
AI Revolutionizes Cancer Care with New Technologies and Treatments

Artificial intelligence (AI) is rapidly transforming cancer care, enhancing research, diagnosis, and treatment. The National Health Service (NHS) has recently announced the deployment of AI tools on an “unprecedented scale”, aiming to provide millions of patients with “faster and smarter care.” This initiative includes a significant trial involving 700,000 women to identify potential signs of breast cancer.
The potential of AI in cancer detection is vast. In August, researchers reported that AI could soon identify throat cancer by analyzing changes in a person’s voice. Last week, scientists revealed advancements in creating a personalized vaccine against melanoma skin cancer, further showcasing AI’s role in cancer treatment.
How AI is Enhancing Cancer Research
The most effective strategies against cancer involve prevention and early detection. Researchers analyze vast amounts of data daily, searching for patterns in genetic information. This process can be time-consuming; however, AI simplifies it significantly.
Professor Nuria Lopez-Bigas from Spain’s Institute for Research in Biomedicine explains, “Before AI, we would look at a patient’s tumour and guess which mutations to experiment on. With AI, we can analyze thousands of tumours from around the world and identify patterns that indicate which mutations drive cancer.” This shift allows scientists to expedite their research by years or even decades.
This year, King’s College London utilized ChatGPT-4 to discover new drug combinations for breast cancer treatment. By sifting through existing studies, the AI suggested 12 untested drug combinations, seven of which showed promise in laboratory tests on cancer cells. Meanwhile, the Institute for Cancer Research trained AI to assess how various medications alter the shape of cancer cells, achieving a remarkable 99 percent accuracy. This advancement could reduce the duration of pre-human testing from three years to just three months.
AI’s Role in Cancer Diagnosis and Treatment
AI’s capabilities are increasingly being adopted in clinical settings to accelerate cancer diagnosis. It can detect anomalies in imaging data that may be invisible to human eyes. The National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) encouraged hospitals to implement AI for mole examinations, utilizing a detection system called DERM. This system compares smartphone images of moles against a comprehensive database to assist doctors in determining their cancerous nature.
Additionally, hospitals are exploring AI’s ability to identify lung, breast, and prostate cancers at earlier stages. AI’s effectiveness is rooted in its capacity to compare new patient data against millions of historical cases within seconds.
Dr. Joe Barnett, a radiologist at the Royal Free NHS Trust in London, states, “AI is helping massively. Instead of needing two radiologists, we can use one plus the AI system.” This approach allows physicians to focus on evaluating the implications of detected masses rather than solely identifying them.
A two-year study involving 3,000 men is currently underway to test similar technology for prostate cancer detection. Researchers at Oregon Health and Science University have developed an algorithm capable of recognizing early signs of throat cancer based on voice recordings.
While AI cannot presently perform cancer treatments, it is enhancing decision-making for healthcare professionals. The focus is on “precision,” “personalized,” and “tailored” treatments that consider individual patients’ genetic profiles. This approach minimizes side effects and increases the likelihood of successful outcomes.
The American Society of Clinical Oncology has introduced a tool similar to ChatGPT that assists doctors by providing a shortlist of treatment options based on patient data and current medical knowledge. Dr. Julie Gralow, a breast cancer specialist, emphasizes the importance of AI in clinical practice, stating, “AI won’t replace oncologists, but those who use it will replace those who don’t.”
AI technology is also being tested in surgical applications, where it may automate routine tasks, thereby allowing surgeons to focus on more complex decisions. Leading robotic surgery manufacturer Intuitiv is employing AI to analyze surgical procedures, providing feedback for improvement. In a groundbreaking achievement, scientists at Johns Hopkins University programmed a robot to conduct imitation surgeries autonomously.
Furthermore, AI is poised to enhance patient monitoring during recovery by integrating wearable sensors that track vital signs with healthcare providers’ systems.
As described by America’s Cancer Research Institute, the intersection of AI and cancer care represents an “emerging revolution” that has the potential to reshape our understanding, diagnosis, and treatment of cancer. Professor Lopez-Bigas anticipates even greater advancements in the near future, stating, “I have a feeling that the biggest leap is yet to come.”
Early detection remains critical for improving cancer survival rates, and various screening programs are available, including cervical, breast, and bowel screenings in England. The NHS encourages eligible individuals to participate in these screenings, as early detection can significantly enhance treatment effectiveness.
By leveraging AI technologies, the landscape of cancer care is evolving, promising improved outcomes for patients and a more efficient healthcare system.
-

 Health3 months ago
Health3 months agoNeurologist Warns Excessive Use of Supplements Can Harm Brain
-

 Health3 months ago
Health3 months agoFiona Phillips’ Husband Shares Heartfelt Update on Her Alzheimer’s Journey
-

 Science2 months ago
Science2 months agoBrian Cox Addresses Claims of Alien Probe in 3I/ATLAS Discovery
-

 Science2 months ago
Science2 months agoNASA Investigates Unusual Comet 3I/ATLAS; New Findings Emerge
-

 Science1 month ago
Science1 month agoScientists Examine 3I/ATLAS: Alien Artifact or Cosmic Oddity?
-

 Entertainment5 months ago
Entertainment5 months agoKerry Katona Discusses Future Baby Plans and Brian McFadden’s Wedding
-

 Science1 month ago
Science1 month agoNASA Investigates Speedy Object 3I/ATLAS, Sparking Speculation
-

 Entertainment4 months ago
Entertainment4 months agoEmmerdale Faces Tension as Dylan and April’s Lives Hang in the Balance
-

 World3 months ago
World3 months agoCole Palmer’s Cryptic Message to Kobbie Mainoo Following Loan Talks
-
 Science1 month ago
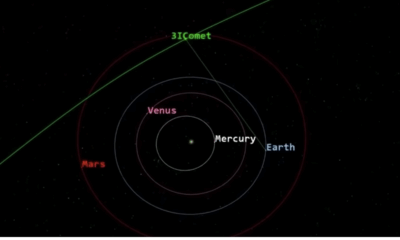
Science1 month agoNASA Scientists Explore Origins of 3I/ATLAS, a Fast-Moving Visitor
-

 Entertainment2 months ago
Entertainment2 months agoLewis Cope Addresses Accusations of Dance Training Advantage
-

 Entertainment3 months ago
Entertainment3 months agoMajor Cast Changes at Coronation Street: Exits and Returns in 2025