Science
Idaho’s Invasive Mussel Eradication Plan Risks Local Wildlife

Efforts to eradicate invasive mussels in Idaho’s Snake River may inadvertently threaten local wildlife. A recent study published in Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry highlights the potential consequences of this eradication strategy, which involves the use of a copper-based molluscicide. The research indicates that the chemical treatment could significantly reduce biodiversity, impacting various freshwater species in the area.
The invasive Dreissenid mussels, including zebra and quagga mussels, were first identified in the United States in the Great Lakes in 1988. Since then, these species have proliferated across many lakes and rivers, leading to severe ecological and economic repercussions. Their presence has disrupted food chains, caused fisheries to collapse, and resulted in an estimated $267 million in mitigation costs for water treatment and electrical plants between 1989 and 2004.
In late 2023, Idaho officials discovered larval and adult quagga mussels in the Snake River near Twin Falls, marking the first occurrence of these invasive species in the Columbia River Basin. In response, the state initiated a plan to eradicate the mussels by applying a copper-based molluscicide, which contains 28.2% copper ethanolamine and 9.1% metallic copper. Approximately 46,000 gallons of this treatment were introduced into the river over a ten-day period.
Researchers conducted a thorough evaluation of the environmental impact of the copper treatment. They collected water samples from seven locations along the Snake River during the treatment period and found that nearly half of the original copper mass dissipated by the end of their observation. Despite this, dissolved copper concentrations remained above toxic levels for more than two weeks, raising concerns about its effect on aquatic life.
The study recorded a significant decline in animal abundance at the treatment sites, with reductions ranging from 54% to 94%. This drop was primarily attributed to the loss of species such as water nymph worms, flatworms, midge flies, freshwater shrimp, and pebblesnails. Alarmingly, some species, including the New Zealand mud snail, the gyro snail, and the tadpole snail, were completely eradicated from the river.
While the treatment did facilitate the emergence of some new organisms, including sludge worms and seed shrimp, the overall impact on biodiversity is concerning. The effects of copper extended nearly 40 miles downstream, potentially jeopardizing federally listed threatened or endangered species in the region. The alteration in species diversity could have serious implications for the diets and habitats of other aquatic animals, particularly protected fish species.
As Idaho continues to grapple with the challenge of invasive mussels, the findings from this research underscore the need for careful consideration of the ecological consequences of eradication efforts. The study serves as a crucial reminder that while the objective is to eliminate harmful species, the methods employed may inadvertently harm other vital components of the ecosystem.
More information on the study can be found in the article titled “Fate and effects to the benthic community of a copper treatment to eradicate invasive mussels in a large western river, USA,” published in Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry in 2025.
-

 Health3 months ago
Health3 months agoNeurologist Warns Excessive Use of Supplements Can Harm Brain
-

 Health3 months ago
Health3 months agoFiona Phillips’ Husband Shares Heartfelt Update on Her Alzheimer’s Journey
-

 Science2 months ago
Science2 months agoBrian Cox Addresses Claims of Alien Probe in 3I/ATLAS Discovery
-

 Science2 months ago
Science2 months agoNASA Investigates Unusual Comet 3I/ATLAS; New Findings Emerge
-

 Science1 month ago
Science1 month agoScientists Examine 3I/ATLAS: Alien Artifact or Cosmic Oddity?
-

 Entertainment5 months ago
Entertainment5 months agoKerry Katona Discusses Future Baby Plans and Brian McFadden’s Wedding
-

 Science1 month ago
Science1 month agoNASA Investigates Speedy Object 3I/ATLAS, Sparking Speculation
-

 Entertainment4 months ago
Entertainment4 months agoEmmerdale Faces Tension as Dylan and April’s Lives Hang in the Balance
-

 World3 months ago
World3 months agoCole Palmer’s Cryptic Message to Kobbie Mainoo Following Loan Talks
-
 Science1 month ago
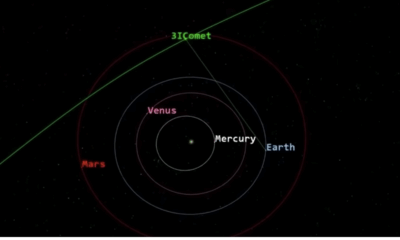
Science1 month agoNASA Scientists Explore Origins of 3I/ATLAS, a Fast-Moving Visitor
-

 Entertainment2 months ago
Entertainment2 months agoLewis Cope Addresses Accusations of Dance Training Advantage
-

 Entertainment3 months ago
Entertainment3 months agoMajor Cast Changes at Coronation Street: Exits and Returns in 2025