Science
NASA Unveils Stunning Images of Interstellar Comet 3I/ATLAS
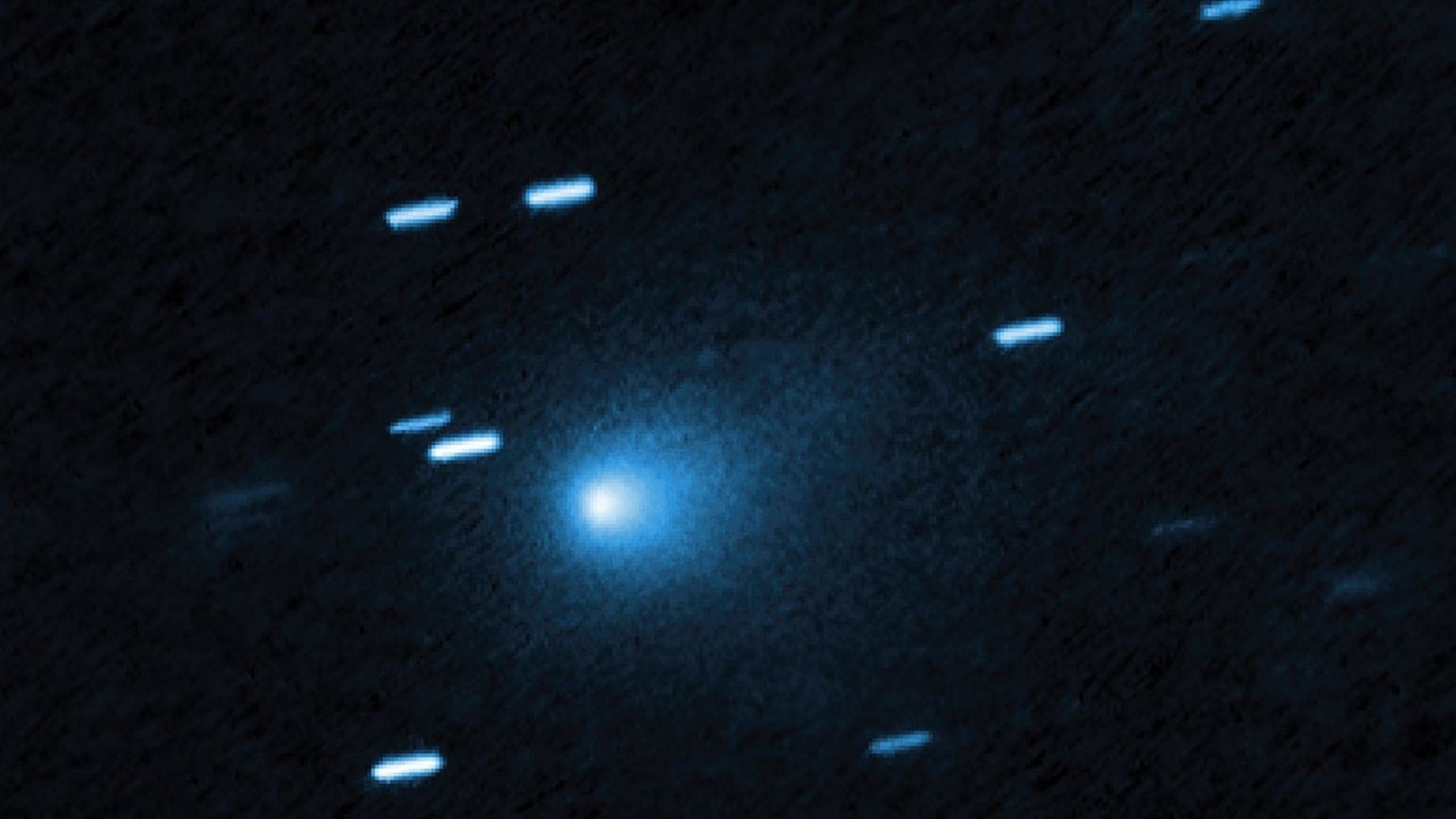

NASA has released remarkable close-up images of the interstellar comet 3I/ATLAS, providing an extraordinary view of this celestial object that originated from beyond our solar system. The newly captured visuals reveal intricate details about the comet’s structure, behavior, and its journey through space, showcasing ancient materials that predate the formation of our Sun.
The images focus particularly on the comet’s dusty halo, known as its coma, along with the streams of gas and dust emanating from its icy nucleus. To obtain these insights, scientists utilized a variety of NASA spacecraft, including probes orbiting Mars, as well as renowned space telescopes like the Hubble Space Telescope and the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST). These tools allowed for multi-angle observations as the comet traveled through the inner solar system.
Close Encounter with Mars
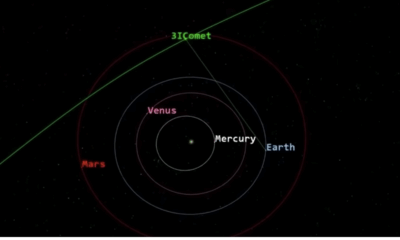
A significant milestone in the comet’s journey occurred in October 2025, when 3I/ATLAS made a close pass by Mars, coming within approximately 19 million miles (30 million kilometers) of the red planet. This proximity enabled orbiting spacecraft to gather crucial data about the comet. During this time, NASA’s Lucy spacecraft, which is on a mission to study Jupiter’s Trojan asteroids, also managed to capture images of the comet’s coma and tail.
Earlier images from the Hubble telescope, taken while 3I/ATLAS was still distant from Mars, depicted a teardrop-shaped cocoon of dust enveloping the comet’s nucleus. These observations indicate that the comet is actively shedding material as it warms in the inner solar system, with the asymmetrical shape of its coma providing further evidence of this process.
Spectroscopic studies, particularly those conducted by the JWST, identified significant quantities of carbon dioxide, water, carbon monoxide, and cyanide in the comet’s composition. These findings are crucial for scientists aiming to understand the makeup of this interstellar visitor.
What Lies Ahead for 3I/ATLAS
One of the key questions surrounding 3I/ATLAS is its closest approach to Earth. According to NASA, this will occur in mid-December 2025, when the comet will pass at a distance of around 167 million miles (269 million kilometers). This distance, equivalent to approximately 1.8 astronomical units (AU), is nearly double the average distance between the Earth and the Sun, ensuring that there is no risk of collision.
Multiple assessments confirm that 3I/ATLAS poses no danger to our planet. Instead, this upcoming close encounter presents a rare opportunity for scientific research. NASA and other space agencies continue to monitor the comet’s behavior and composition through both ground-based and space telescopes as it travels swiftly through our solar system.
Following its December flyby, 3I/ATLAS is expected to return to interstellar space, never to return to our solar system. As such, this comet serves as a unique messenger from another star system, potentially offering insights into comet formation elsewhere in the galaxy.
-

 Health3 months ago
Health3 months agoNeurologist Warns Excessive Use of Supplements Can Harm Brain
-

 Health3 months ago
Health3 months agoFiona Phillips’ Husband Shares Heartfelt Update on Her Alzheimer’s Journey
-

 Science1 month ago
Science1 month agoBrian Cox Addresses Claims of Alien Probe in 3I/ATLAS Discovery
-

 Science1 month ago
Science1 month agoNASA Investigates Unusual Comet 3I/ATLAS; New Findings Emerge
-

 Science4 weeks ago
Science4 weeks agoScientists Examine 3I/ATLAS: Alien Artifact or Cosmic Oddity?
-

 Science4 weeks ago
Science4 weeks agoNASA Investigates Speedy Object 3I/ATLAS, Sparking Speculation
-

 Entertainment4 months ago
Entertainment4 months agoKerry Katona Discusses Future Baby Plans and Brian McFadden’s Wedding
-

 Entertainment4 months ago
Entertainment4 months agoEmmerdale Faces Tension as Dylan and April’s Lives Hang in the Balance
-

 World3 months ago
World3 months agoCole Palmer’s Cryptic Message to Kobbie Mainoo Following Loan Talks
-
 Science4 weeks ago
Science4 weeks agoNASA Scientists Explore Origins of 3I/ATLAS, a Fast-Moving Visitor
-

 Entertainment4 months ago
Entertainment4 months agoLove Island Star Toni Laite’s Mother Expresses Disappointment Over Coupling Decision
-

 Entertainment3 months ago
Entertainment3 months agoMajor Cast Changes at Coronation Street: Exits and Returns in 2025









