Science
Novel RNA Chaperone Discovered in Poxvirus Assembly Process
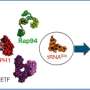
A groundbreaking study from the University of Würzburg has revealed a previously unknown RNA chaperone that plays a critical role in the assembly of a key protein complex in poxviruses. This discovery sheds light on the unique strategies these viruses employ to replicate rapidly after infecting a host cell.
Researchers have identified that this RNA chaperone assists in the proper folding and assembly of proteins necessary for the virus’s life cycle. Understanding this mechanism could pave the way for developing innovative antiviral agents aimed at combating poxvirus infections, which have historically posed significant health threats.
Uncovering the Role of RNA Chaperones
The research highlights the importance of RNA chaperones, which are molecules that facilitate the proper configuration of RNA structures. The team at Würzburg found that this specific chaperone interacts directly with viral RNA, aiding the assembly of viral proteins into functional complexes. This interaction is crucial for the virus to successfully hijack the host’s cellular machinery for its replication.
The study indicates that poxviruses have evolved these chaperones to enhance their adaptability and efficiency in infection. As these viruses can lead to serious diseases in humans and animals, understanding their assembly mechanisms is vital for public health and safety.
Implications for Antiviral Development
The findings could create a foundation for new therapeutic strategies against poxviruses. By targeting the RNA chaperone or its interactions, scientists may be able to disrupt the viral replication process. This approach could serve as a novel avenue for antiviral drug development, potentially leading to effective treatments for infections caused by these resilient viruses.
As the research continues, the implications of these findings extend beyond just poxviruses. The mechanisms unveiled may also provide insights into other viral families, further contributing to the global fight against viral diseases. The study, published in 2023, emphasizes the need for continued research into viral biology and the development of innovative treatment options to safeguard public health.
-

 Health3 months ago
Health3 months agoNeurologist Warns Excessive Use of Supplements Can Harm Brain
-

 Health3 months ago
Health3 months agoFiona Phillips’ Husband Shares Heartfelt Update on Her Alzheimer’s Journey
-

 Science2 months ago
Science2 months agoBrian Cox Addresses Claims of Alien Probe in 3I/ATLAS Discovery
-

 Science2 months ago
Science2 months agoNASA Investigates Unusual Comet 3I/ATLAS; New Findings Emerge
-

 Science1 month ago
Science1 month agoScientists Examine 3I/ATLAS: Alien Artifact or Cosmic Oddity?
-

 Entertainment5 months ago
Entertainment5 months agoKerry Katona Discusses Future Baby Plans and Brian McFadden’s Wedding
-

 Science1 month ago
Science1 month agoNASA Investigates Speedy Object 3I/ATLAS, Sparking Speculation
-

 Entertainment4 months ago
Entertainment4 months agoEmmerdale Faces Tension as Dylan and April’s Lives Hang in the Balance
-

 World3 months ago
World3 months agoCole Palmer’s Cryptic Message to Kobbie Mainoo Following Loan Talks
-
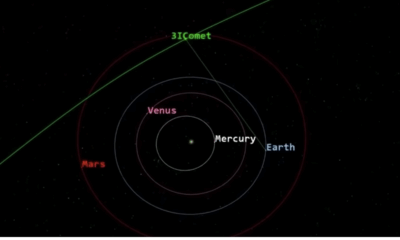
 Science1 month ago
Science1 month agoNASA Scientists Explore Origins of 3I/ATLAS, a Fast-Moving Visitor
-

 Entertainment2 months ago
Entertainment2 months agoLewis Cope Addresses Accusations of Dance Training Advantage
-

 Entertainment3 months ago
Entertainment3 months agoMajor Cast Changes at Coronation Street: Exits and Returns in 2025