Science
Quantum Computing Advances Through New Performance Metrics
Researchers are advancing the field of quantum computing by establishing new performance metrics aimed at achieving practical quantum advantage. Major technology companies, including Google, Amazon, IBM, and Microsoft, along with innovative startups, are shifting quantum computing from theoretical research to a viable commercial landscape. The ultimate goal is to create quantum computers capable of executing tasks significantly faster than classical computers, thus addressing complex scientific, industrial, and commercial challenges.
Benchmarking Quantum Performance
As the quantum computing supply chain matures, it is crucial for government laboratories and academic institutions to focus on foundational research. This involves developing quantum hardware and software technologies, supported by theoretical principles and experimental systems. A significant initiative in this area is a comprehensive research collaboration in the United Kingdom that has been underway for the past four years. This project aims to create a detailed taxonomy of metrics and benchmarks to evaluate quantum computers against classical systems and among various quantum platforms.
Funded by the National Quantum Computing Centre (NQCC) as part of the National Quantum Technologies Programme, this initiative is spearheaded by scientists at the National Physical Laboratory (NPL). The consortium, which includes experts from several universities, is tackling the diverse landscape of quantum hardware, which ranges from superconducting circuits to trapped ions and photonic processors. Ivan Rungger, a principal scientist at NPL, emphasizes the importance of this benchmarking effort for fostering trust, comparability, and commercial adoption of quantum technologies.
Challenges in Metric Standardization
While some classical performance metrics can be adapted for quantum computers—like operational speed and error rates—the complexity of quantum systems necessitates the development of unique benchmarks. The proliferation of specialized metrics in the past decade has made it challenging to navigate existing literature. Variations in metrics often lead to difficulties in making objective comparisons, which in turn impedes progress toward achieving quantum advantage.
Rungger states that many benchmarking methods yield similar qualitative performance assessments, yet differences in technical implementations complicate quantitative comparisons. The primary focus is to streamline and rationalize metrics into a minimal, representative set that can be agreed upon by manufacturers, algorithm developers, and end-users. The goal is to establish common approaches to fairly evaluate quantum computers from different vendors.
The ongoing review has resulted in a comprehensive collection of metrics that covers hardware performance to application-level assessments. Each metric is accompanied by a consistent format, including definitions, methodologies, and limitations, along with an open-source software package for practical evaluations. This repository is designed to evolve, reflecting community-driven advancements in the field.
As the quantum landscape continues to develop, the role of standardization becomes increasingly vital. International standards organizations have begun to explore areas ripe for standardization, which will assist manufacturers, users, and investors in evaluating the performance of various quantum computing components.
Deep Lall, a quantum scientist at NPL, highlights the substantial interest in the UK’s benchmarking efforts, noting that they are shaping the international dialogue surrounding quantum standards. Presentations at international meetings and workshops have facilitated widespread engagement, allowing for collaborative discussions on best practices in benchmarking.
Cyrus Larijani, head of the quantum program at NPL, reinforces the significance of evidence-based decision-making as the field advances. By grounding strategic choices in robust measurement science, the aim is to ensure that developments in quantum technology yield meaningful impacts across various industries.
The work conducted by the NPL and its partners signifies a crucial step in the evolution of quantum computing. As the community continues to refine its understanding of performance metrics, the collaborative effort to standardize these benchmarks is expected to enhance the pace of innovation and ultimately lead to practical quantum advantage.
For further insights into this research, see the full study by Deep Lall et al. titled, “A review and collection of metrics and benchmarks for quantum computers: definitions, methodologies and software,” published in March 2025.
-

 Health3 months ago
Health3 months agoNeurologist Warns Excessive Use of Supplements Can Harm Brain
-

 Health3 months ago
Health3 months agoFiona Phillips’ Husband Shares Heartfelt Update on Her Alzheimer’s Journey
-

 Science2 months ago
Science2 months agoBrian Cox Addresses Claims of Alien Probe in 3I/ATLAS Discovery
-

 Science2 months ago
Science2 months agoNASA Investigates Unusual Comet 3I/ATLAS; New Findings Emerge
-

 Science1 month ago
Science1 month agoScientists Examine 3I/ATLAS: Alien Artifact or Cosmic Oddity?
-

 Entertainment5 months ago
Entertainment5 months agoKerry Katona Discusses Future Baby Plans and Brian McFadden’s Wedding
-

 Science1 month ago
Science1 month agoNASA Investigates Speedy Object 3I/ATLAS, Sparking Speculation
-

 Entertainment4 months ago
Entertainment4 months agoEmmerdale Faces Tension as Dylan and April’s Lives Hang in the Balance
-

 World3 months ago
World3 months agoCole Palmer’s Cryptic Message to Kobbie Mainoo Following Loan Talks
-
 Science1 month ago
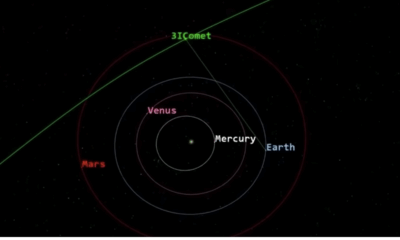
Science1 month agoNASA Scientists Explore Origins of 3I/ATLAS, a Fast-Moving Visitor
-

 Entertainment2 months ago
Entertainment2 months agoLewis Cope Addresses Accusations of Dance Training Advantage
-

 Entertainment3 months ago
Entertainment3 months agoMajor Cast Changes at Coronation Street: Exits and Returns in 2025