Science
Asteroid Belt Thinning: Implications for Earth and Beyond
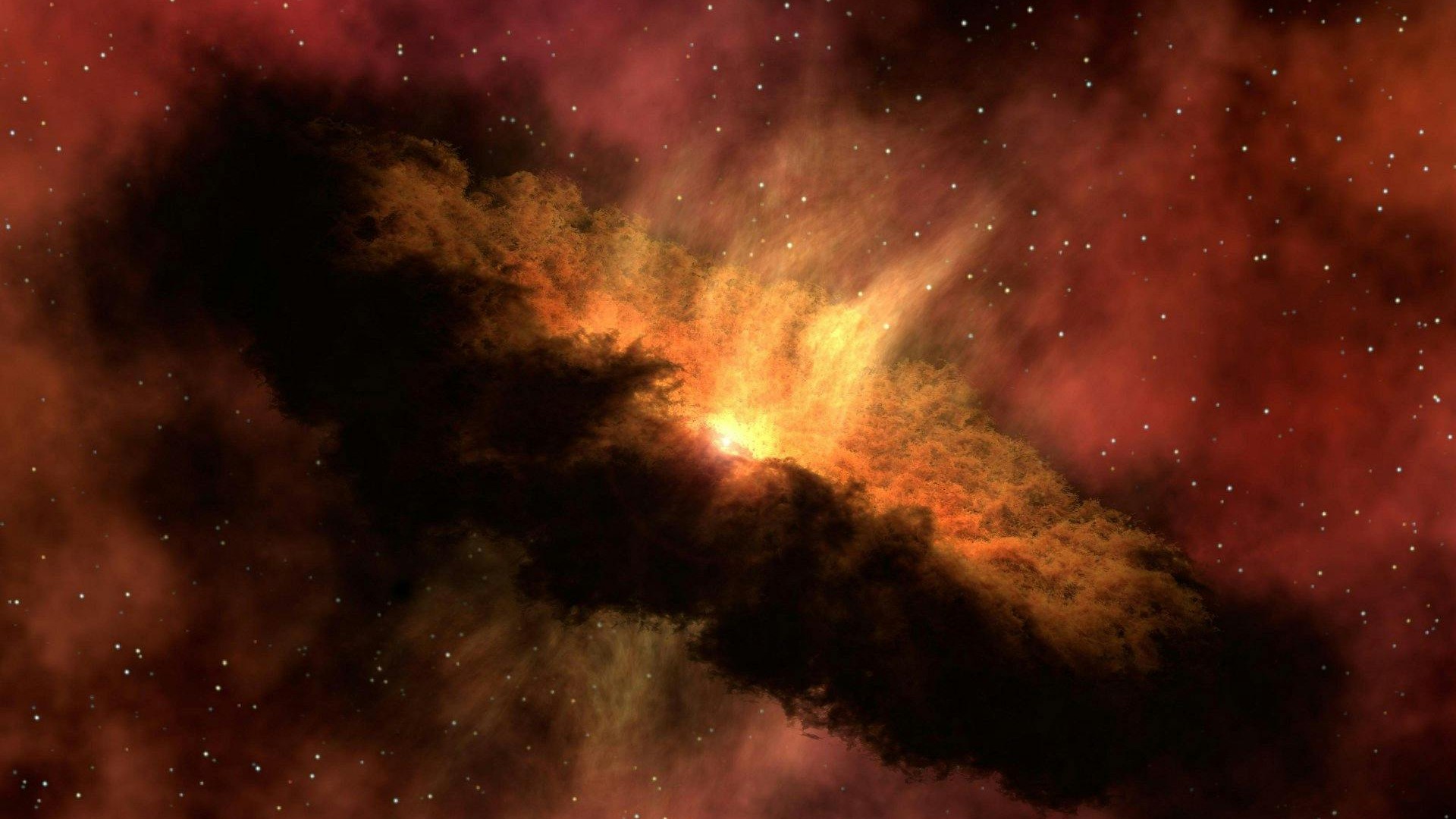

Research reveals that the asteroid belt, located between Mars and Jupiter, is experiencing a significant reduction in mass. A recent study published by a team of researchers indicates that this once-dense region of rocky fragments is gradually thinning out, raising questions about its implications for Earth and the future of our solar system.
The asteroid belt formed billions of years ago from remnants of material that failed to coalesce into a planet. Initially, it served as a rich reservoir of cosmological history, but the study suggests that a substantial portion of this material has been lost over time. Factors such as collisions and gravitational influences from Jupiter have contributed to the steady erosion of the belt.
Concerning Findings on Asteroid Loss
The study highlights alarming statistics: only a fraction of the original material in the asteroid belt remains intact. Researchers found that the continuous interactions and gravitational tugs have reshaped the belt’s population, leading to a gradual decline that is not being offset by the formation of new asteroids. This phenomenon signifies a long-term change in the asteroid belt’s composition and character.
Despite the thinning belt, the immediate impact on Earth is minimal. Nonetheless, over time, some of the lost material migrates toward our planet in the form of meteorites. Although most of these meteorites burn up harmlessly upon entering the atmosphere, some do reach the surface, contributing to the ongoing narrative of Earth’s dynamic geological history.
Broader Implications for Cosmic Understanding
The findings of this research extend beyond the confines of our solar system. Scientists suggest that similar processes of erosion and transformation may occur in other planetary systems across the galaxy. The ongoing changes in the asteroid belt provide essential insights into planetary evolution, allowing astronomers to better understand how solar systems form, age, and redistribute their building blocks over extensive timescales.
As the asteroid belt continues to thin, it remains a valuable source of scientific discovery. The gradual transformation serves as a cosmic clock, reminding us that even the most enduring celestial features are subject to change. By studying these processes, researchers gain a deeper understanding of forces that influence not just our solar system, but potentially countless others throughout the universe.
In conclusion, while the thinning of the asteroid belt presents no immediate dangers to life on Earth, it is a critical aspect of our cosmic environment. The changes within this region reflect broader trends in planetary systems and serve as a reminder of the dynamic nature of our universe.
-

 Health3 months ago
Health3 months agoNeurologist Warns Excessive Use of Supplements Can Harm Brain
-

 Health4 months ago
Health4 months agoFiona Phillips’ Husband Shares Heartfelt Update on Her Alzheimer’s Journey
-

 Science2 months ago
Science2 months agoBrian Cox Addresses Claims of Alien Probe in 3I/ATLAS Discovery
-

 Science2 months ago
Science2 months agoNASA Investigates Unusual Comet 3I/ATLAS; New Findings Emerge
-

 Science2 months ago
Science2 months agoScientists Examine 3I/ATLAS: Alien Artifact or Cosmic Oddity?
-

 Entertainment2 months ago
Entertainment2 months agoLewis Cope Addresses Accusations of Dance Training Advantage
-

 Entertainment5 months ago
Entertainment5 months agoKerry Katona Discusses Future Baby Plans and Brian McFadden’s Wedding
-

 Science2 months ago
Science2 months agoNASA Investigates Speedy Object 3I/ATLAS, Sparking Speculation
-

 Entertainment5 months ago
Entertainment5 months agoEmmerdale Faces Tension as Dylan and April’s Lives Hang in the Balance
-

 World3 months ago
World3 months agoCole Palmer’s Cryptic Message to Kobbie Mainoo Following Loan Talks
-

 World4 weeks ago
World4 weeks agoBailey and Rebecca Announce Heartbreaking Split After MAFS Reunion
-
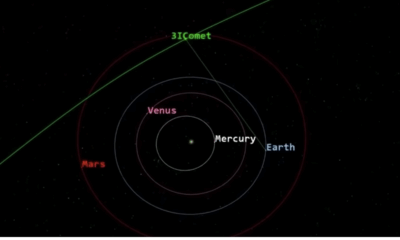
 Science2 months ago
Science2 months agoNASA Scientists Explore Origins of 3I/ATLAS, a Fast-Moving Visitor









